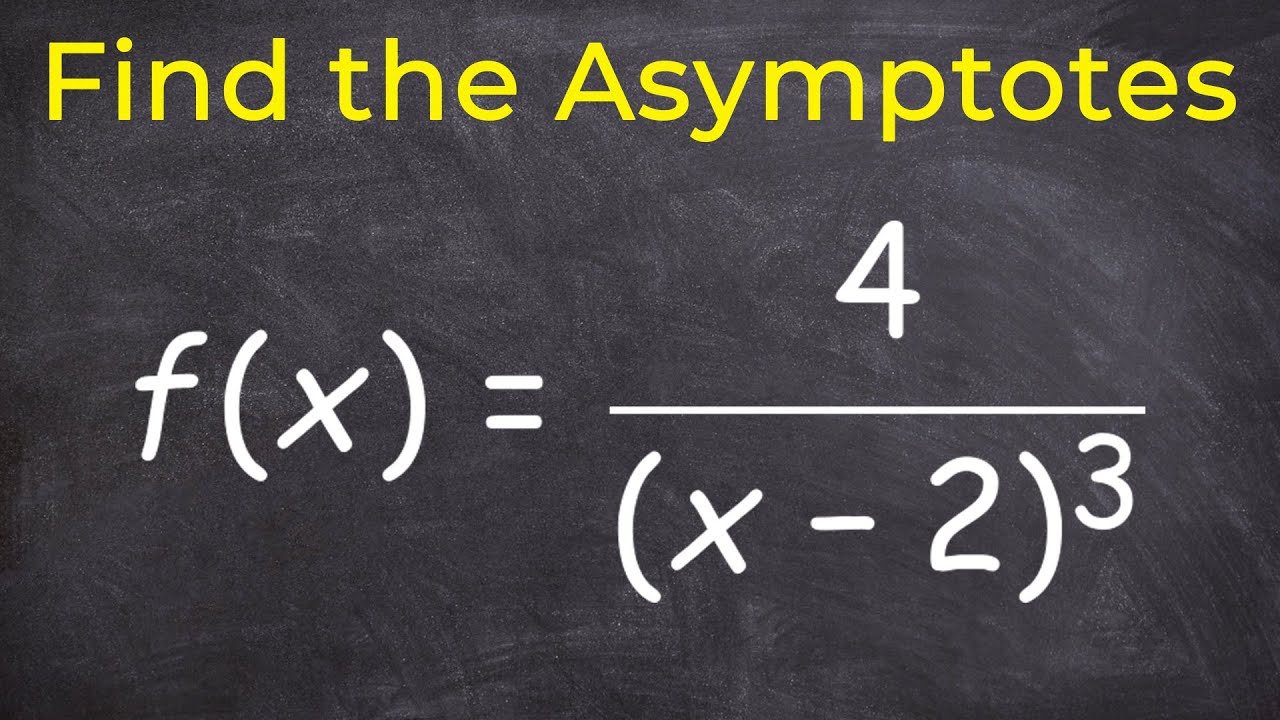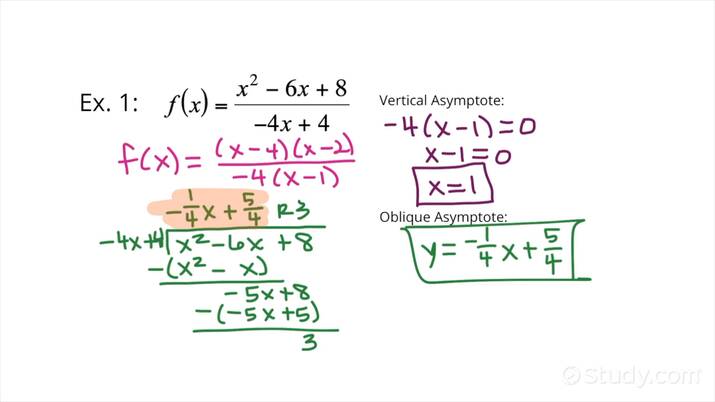
How to Effectively Find Asymptotes: A Simple Guide for 2025
How to Effectively Find Asymptotes: A Simple Guide for 2025
Understanding asymptotes is crucial for anyone studying mathematics, especially in calculus. Asymptotes are lines that a graph approaches but never actually touches, illustrating the concept of limits in calculus. This guide will walk you through the definition and types of asymptotes, such as vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptotes, and provide clear methods on how to find asymptotes for different functions.
Asymptote Definition and Importance
An asymptote can be defined as a line that a graph approaches as it heads towards infinity in certain directions. The importance of identifying asymptotes lies in their ability to provide insights into the behavior of functions, particularly rational functions. Understanding asymptotes helps in graphing functions accurately, as they indicate how the graph behaves near undefined points or at infinity. By analyzing limits, students can gain clarity on the long-term trajectory of a graph.
Types of Asymptotes
There are three primary types of asymptotes: vertical asymptotes, horizontal asymptotes, and oblique asymptotes. Each serves a unique role in illustrating different behaviors of functions. Vertical asymptotes occur when the function approaches infinity as the input approaches a specific value. Horizontal asymptotes indicate the function’s value as the input approaches infinity. Lastly, oblique asymptotes are applicable when a graph rises or falls indefinitely without leveling off horizontally, typically seen in rational functions with a higher degree in the numerator. Recognizing these distinctions is essential for solving asymptotes effectively.
Visualizing Asymptotes
To really grasp the concept of asymptotes, visualizing them is highly beneficial. The graphical representation reveals how the curve behaves near the asymptotes, showcasing approaches that lead into infinity without crossing these important lines. Using graphical calculators or software can profoundly assist in graphing functions that have asymptotic behavior, allowing students to observe the intersections, distances, and behaviors of the curves. Understanding how to graph asymptotes not only enhances learning but also makes interpreting functions easier.
Significance of Asymptotes in Graphing
Asymptotes hold significant value in graphing functions as they guide the plotting of data points. This is especially important in calculus when studying process continuity and understanding function discontinuities. By identifying vertical and horizontal asymptotes, one can sketch the general shape of a function, enhancing clarity in presentation and accuracy in problem-solving. An effective understanding of asymptotes is fundamental to navigating through complex problems in calculus and beyond.
How to Find Asymptotes
Knowing how to find asymptotes is essential for students working with rational functions and calculus concepts. The process typically involves limits and analyzing characteristics of functions, including graphical behavior at specified points.
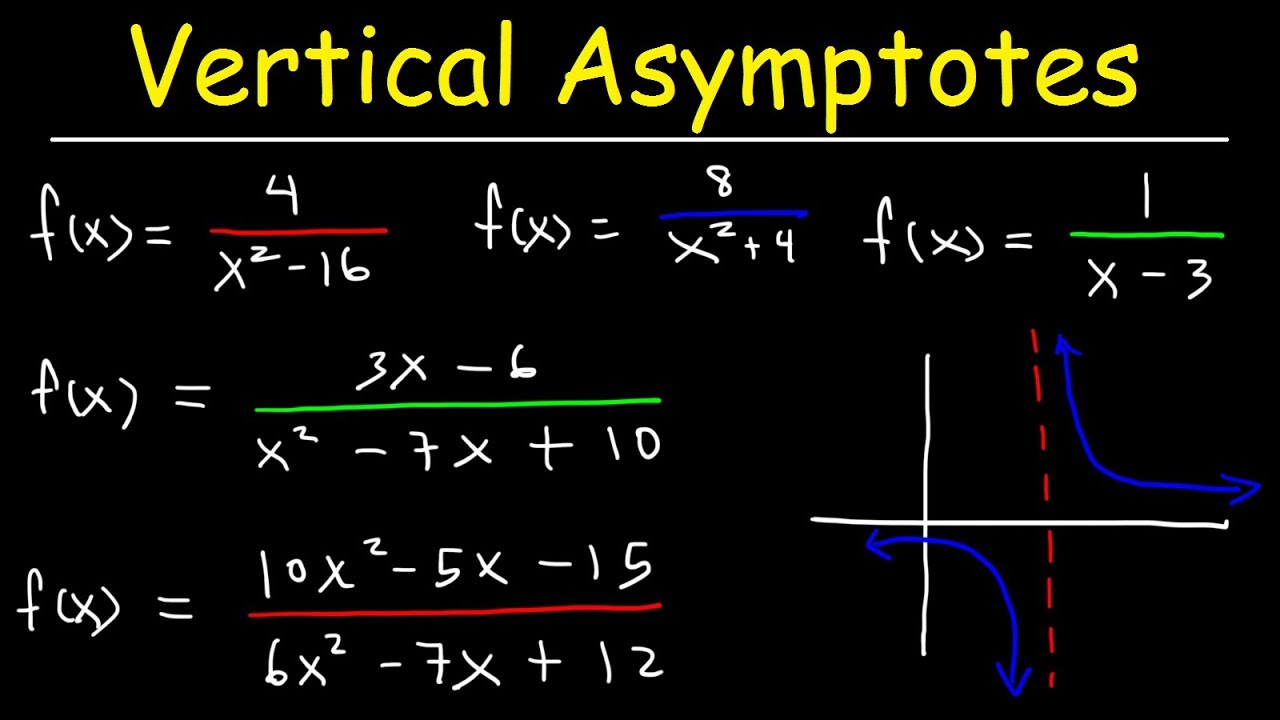
Finding Vertical Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes can be discovered by setting the denominator of a rational function equal to zero and solving for the variable. For example, consider the function \(f(x) = \frac{1}{x-3}\). Here, setting the denominator \(x – 3 = 0\) reveals a vertical asymptote at \(x = 3\). As the function approaches this value, \(f(x)\) moves towards infinity in the positive or negative direction, illustrating the classic behavior near vertical asymptotes. Always ensure to check for any common factors in the numerator to confirm the asymptote’s presence appropriately.
Determining Horizontal Asymptotes
To find horizontal asymptotes, you must analyze the limits of a function as \(x\) approaches infinity or negative infinity. Specifically, if \(f(x)\) involves ratios of polynomials, you find the highest degree terms. For instance, with \(f(x) = \frac{4x^2 + 2}{2x^2 + 3}\), both the numerator and denominator have degrees of 2. Therefore, the horizontal asymptote can be determined by evaluating the leading coefficients, yielding \(y = \frac{4}{2} = 2\). Understanding limits is vital in mastering this part of finding asymptotes.
Understanding Oblique Asymptotes
Oblique asymptotes appear when the degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator by one. In such cases, polynomial long division can reveal the behavior of the graph at infinity. For example, if we take \(f(x) = \frac{x^3 + 3x^2 + 2}{x^2 + 1}\), performing long division will give you a linear equation that represents the oblique asymptote. Recognizing whether a function has an oblique asymptote aids in predicting how the graph behaves as it stretches towards the positive or negative infinity, proving essential to comprehension in calculus domains.
Solving Asymptote Problems
Working with asymptotes involves a series of analytical techniques that can sometimes pose challenges. However, familiarizing oneself with common issues can aid in mastering asymptote problems.
Common Mistakes in Asymptote Identification
One of the common pitfalls in identifying asymptotes includes confusing vertical asymptotes with horizontal ones. Additionally, failing to recognize when a common factor cancels can lead to incorrect conclusions about the presence of an asymptote. Always evaluate the function thoroughly, considering all approaches to ensure accuracy in identifying behavior near asymptotic lines. This attention to detail can greatly mitigate the chances of mistakes in calculus and beyond.
Using Derivatives to Analyze Asymptotes
Another strategy for solving asymptote problems includes utilizing derivatives. By finding the first derivative of a function, one can identify critical points that may indicate changes in behavior around asymptotes. For instance, applying the first derivative test can help determine increasing or decreasing intervals of functions, providing further insight into a function’s eventual approach towards vertical or horizontal asymptotes. Recognizing this technique is valuable for deepening understanding among calculus students.
Application of Key Concepts
Integrating key concepts into problems involving asymptotes involves not just recognition but effective applications. Practicing with varying rational functions can bolster skills in identifying and solving for asymptotes. Education resources, quizzes, and dynamic learning tools also serve to enhance understanding. Make use of online asymptote calculators, which allow for real-time feedback and exploration of different functions. Learning asymptotes requires perseverance, continual practice, and thorough grasping of core concepts for academic success in calculus.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the definition, significance, and different types of asymptotes—vertical, horizontal, and oblique—is crucial for graphing functions.
- Finding asymptotes involves determining points that lead to undefined behaviors clearly: vertical (denominator = 0), horizontal (limits as x approaches infinity), and oblique (higher degree numerator).
- Recognizing common mistakes and applying derivatives can reinforce your understanding of function behavior near asymptotes.
- Practice with a variety of problems, resources, and analytical techniques is essential for mastering asymptotes.
FAQ
1. What are the basic types of asymptotes?
The basic types of asymptotes include vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptotes. Vertical asymptotes indicate where the function approaches infinity as the input approaches a certain value. Horizontal asymptotes represent the behavior of the function as the input increases indefinitely, while oblique asymptotes occur when the function tends towards a non-horizontal line as infinity is approached.
2. How do I identify vertical asymptotes in a function?
To identify vertical asymptotes, you must find the values that make the denominator of a rational function equal to zero. This indicates points where the function does not exist, leading to vertical asymptotic behavior. Always check if these points are canceled out by the numerator, as this would negate the asymptotic presence.
3. Can horizontal asymptotes change?
Horizontal asymptotes rarely change unless the definition of the function itself is altered, as they signify the eventual behavior of a function as one approaches infinity. Understanding the leading coefficients in polynomial degrees remains key to establishing the consistency of horizontal asymptotes.
4. What’s the role of limits in finding asymptotes?
Limits provide essential information about the behavior of functions as inputs approach specific values or infinity. By determining limits of rational functions, one can distinctly ascertain both vertical and horizontal asymptotes effectively.
5. How can graphical representation help in understanding asymptotes?
Graphical representation of asymptotes helps visualize the behavior of outputs as inputs reach undefined points or extremes. Using graphing calculators can provide direct insights and make learning about asymptotes easier, paving the way for effective problem-solving.
6. What online tools assist with understanding asymptotes?
There are various online resources, including graphing calculators and interactive tools specifically designed to help students explore asymptotes comprehensively. Many websites offer tutorials, quizzes, and practice problems that can deepen understanding and provide real-time feedback.
7. Why is studying asymptotes important?
Studying asymptotes is foundational in mathematics as they illustrate key behaviors of functions, particularly in calculus. Asymptotes help in understanding continuity, limits, and graphing, and are crucial in solving complex mathematical problems across various applications.
For more in-depth information about how to find asymptotes, you can also check out resources and articles detailing the applications and techniques above: Introduction to Asymptotes or Graphing Asymptotes Tutorial.