Practical Guide to How to Calculate Percent Yield in 2025: Improve Your Chemistry Skills
Practical Guide to How to Calculate Percent Yield in 2025: Improve Your Chemistry Skills
Understanding Percent Yield and Its Importance in Chemistry
Percent yield is a cornerstone concept in chemistry that reflects the efficiency of a chemical reaction. In simpler terms, it compares the actual yield of a reaction—the amount of product actually obtained—to the theoretical yield, which is the maximum amount of product that could be produced under ideal conditions. Knowing how to **calculate percent yield** allows chemists to assess the performance and applicability of reactions in both laboratory and industrial settings. Moreover, understanding yield dynamics aids in **yield optimization**, enabling better resource management and process enhancement.
Theoretical Yield vs. Actual Yield
The **theoretical yield** is a calculated value based on stoichiometry derived from the balanced chemical equations. It indicates the maximum amount of product that can be formed when limiting reactants are completely consumed. Conversely, the **actual yield** is the amount of product actually collected from the experiment. Discrepancies between the two—often resulting in a lower **percent yield**—can stem from experimental errors, incomplete reactions, or side reactions consuming reactants. Understanding these differences and calculating percent yield is essential for evaluating **reaction efficiency** and refining chemical processes.
Percent Yield Formula and Yield Calculation
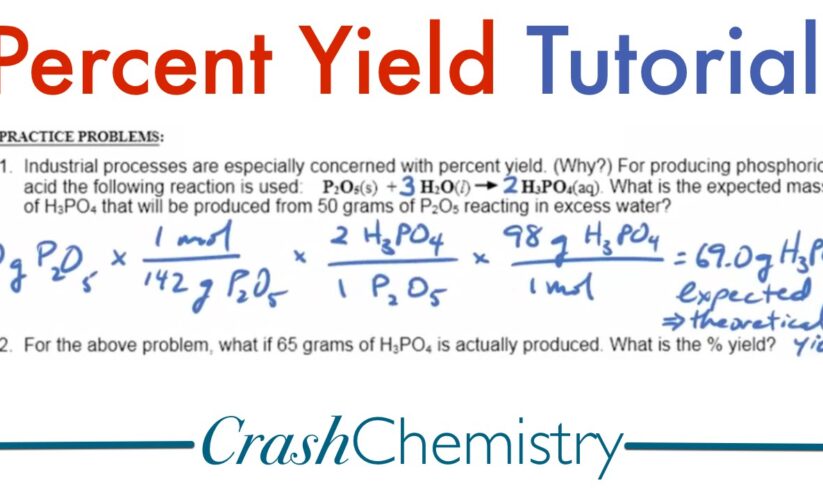
The formula for calculating percent yield is straightforward and is expressed as: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%. To perform a yield assessment, begin by determining both the actual and theoretical yields for your reaction. For instance, if the theoretical yield from a synthesis reaction is 10 grams but only 8 grams were collected, the percent yield would be calculated as follows: Percent Yield = (8 g / 10 g) × 100% = 80%. This calculation provides insight into the **yield dynamics** and helps in determining whether improvements to reaction conditions are necessary.
Strategies to Improve Yield Percentage
Optimizing **yield percentage** is a fundamental goal in chemical experimentation. By implementing certain strategies, chemists can often reduce yield losses and boost the efficiency of reactions. This not only improves laboratory protocols but also reduces waste and operational costs in larger production scenarios. Below, we explore several practical approaches for maximizing yield.
Factors Affecting Yield in Chemical Reactions
A variety of factors can significantly impact chemical yield. These include the purity of reactants, reaction time, temperature, and pressure conditions. For instance, higher temperatures may favor certain reactions but could also induce competing side reactions that detract from the overall yield. Maintaining optimal conditions is critical for achieving desired outcomes and should be incorporated into the **yield evaluation methods** employed in laboratories.
Yield Optimization Strategies
Employing **yield optimization strategies** can involve tweaking experimental conditions or employing techniques such as catalyst use to enhance productivity. Regularly collecting and analyzing **yield data** can help in recognizing patterns, thereby improving **yield testing** and ultimately leading to increased performance metrics. Integrating digital analytics in evaluating yield against set benchmarks can also provide insight into adjustments needed for ongoing experiments.
Practical Example of Yield Improvement
Consider a situation where a student performs a reaction to synthesize a compound and notices a lower-than-expected yield due to unreacted starting materials. By analyzing the experimental setup, the student might discover that opting for a slightly elevated temperature significantly improves reactions by providing the molecules with more energy, thus enhancing the chances of collision and reaction. This illustrates how monitoring **yield protocols** can effectively lead to a better understanding of yield performance and improvement opportunities.
Common Issues with Percent Yield Calculations
While calculating percent yield, various challenges and misunderstandings can arise. Identifying these issues plays a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy of yield assessments and optimizing various laboratory operations.
Yield Miscalculations and Their Impact
Yield miscalculations can occur for reasons such as inaccuracies in measurements of reactants or products, or not accounting for material loss during transfer. For example, if a chemist captures only part of a product during filtration, this can result in a **lower yield calculation**. Therefore, meticulous measurements and proper handling of materials are vital for achieving accurate results in yield statistics and ensuring useful conclusions can be drawn from yield assessments.
Addressing Yield Variances
Variability in yield can also arise from experimental conditions that inadvertently change throughout the process. Factors such as environmental conditions—including humidity or ambient temperature—may alter reaction pathways or product stability. Establishing more robust standards for **yield evaluation processes** can marginalize these variations, ensuring consistently better reaction outcomes by controlling experimental variables more effectively.
Utilizing Yield Data Analysis
Effective yield data analysis entails regular compilation and review of yield records. By utilizing **yield assessment methods**, laboratory personnel can identify trends, correct deviations, and ultimately optimize the yield over time. Analyzing this data empowers teams to refine procedures, improving **production yield** within specific parameters to appreciate the overall efficiency of the methodology being utilized.
Key Takeaways for Calculating and Improving Percent Yield
Successfully navigating the concept of percent yield involves understanding not only how to **calculate percent yield**, but also getting familiar with what influences it and how to improve it effectively. Employing systematic evaluations and implementing best practices for recording and analyzing yield can greatly enhance both individual lab experiences and broader production outcomes.
FAQ
1. What is the definition of percent yield?
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction, represented as the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield expressed as a percentage. Calculating **percent yield** helps chemists assess how well a reaction performed compared to its maximum potential output.
2. How can I calculate percent yield in a reaction?
To calculate the percent yield, use the formula: Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%. For example, if the theoretical yield is 50 grams and the actual yield is 40 grams, the percent yield would be (40 g / 50 g) × 100% = 80%.
3. Why is determining yield important in chemical experiments?
Determining yield is important because it directly informs researchers about the efficiency and success of their reactions. It sheds light on **yield effectiveness** and can highlight areas for improvement to refine processes further.
4. What common factors can decrease yield?
Common factors that may decrease yield include incomplete reactions, side reactions consuming reactants, measurement inaccuracies, and loss of material during product isolation. Optimizing these factors is essential for **yield optimization**.
5. How does temperature affect yield?
Temperature can have a profound impact on yield by influencing reaction rates and the stability of products. Elevated temperatures may increase yields in some cases by providing more energy for reactants to overcome activation barriers, but they can also promote unwanted side reactions. Always factor in temperature when conducting yield analysis.
6. Can theoretical vs. actual yield be impacted by chemical purity?
Yes, the purity of reactants significantly affects theoretical vs. actual yield comparisons. Impure reactants can lead to lower actual yields, which would result in a reduced percent yield and skew the **yield assessment methods** used to evaluate the successful completion of a reaction.
7. What are yield optimization strategies in practice?
Yield optimization strategies can include using catalysts, altering reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure), and employing more efficient purification methods to ensure more of the desired product is obtained. Continuous analysis of yield data can also help streamline experimentation processes for improved yield results.