Effective Guide to How to Do Synthetic Division: Master It in 2025!
Effective Guide to How to Do Synthetic Division: Master It in 2025!
Synthetic division is a potent tool within the realm of polynomial division. For students and enthusiasts of algebra looking to enhance their skills, understanding synthetic division can significantly streamline the process of dividing polynomials. This comprehensive guide will take you through the essential concepts and practical steps to master synthetic division effectively in 2025.
Understanding Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is a simplified form of long division specifically designed for dividing polynomials. In contrast to traditional long division techniques, it provides a quicker and often easier method, especially when dividing by linear factors. To start with, let’s understand the key components involved: the dividend and the divisor. The divisor of the polynomial division must be a first-degree polynomial of the form (x – r), where r is known as the root or the zero of the polynomial. This form is crucial for applying the synthetic division formula.
The Synthetic Division Method
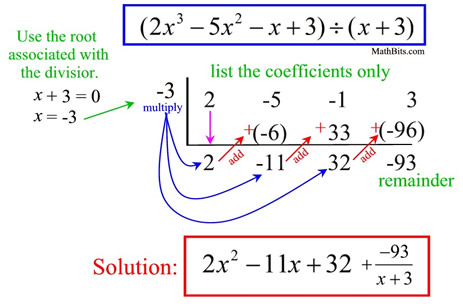
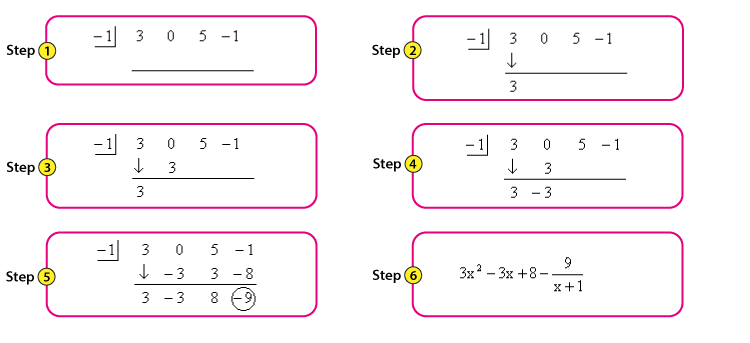
The synthetic division method operates in a few simple steps. First, write down the coefficients of the dividend, ensuring to account for any missing degrees by including zeros for their coefficients. Next, set up the process by identifying your divisor’s value from the root associated with your linear factor. The mechanics of calculating the digest forms involve bringing down the leading coefficient, multiplying, and adding consecutively. This sequence leads to the formation of the remainder, which indicates whether the division produces a whole number of polynomial orders or an additional term. Let’s dive deeper into the steps involved.
Synthetic Division Steps
The following synthetic division steps outline the entire process to promote understanding and proficiency:
- Layout the coefficients: Prepare a row with the coefficients of the dividend.
- Identify your divisor: Determine the root of the divisor to begin the set-up.
- Bring down the leading coefficient: Start the process by bringing the leading coefficient directly down into your working row.
- Multiply and Add: Multiply the brought down number by the root (from the divisor) and add it to the next coefficient. Continue this process for all coefficients.
- Find the remainder: Once all coefficients have been processed, the last number you obtain indicates your remainder. This step defines the success of your synthtic division.
By systematically applying these steps, students will find themselves significantly more adept in performing synthetic division, laying a strong foundation for further exploration in polynomial functions.
Common Applications of Synthetic Division
Synthetic division serves various purposes in algebra and higher mathematics. Moreover, it sees frequent use in operations like evaluating the coefficients of polynomial expressions and transforming them into simpler forms.
Synthetic Division in Solving Polynomial Equations
One of the most valuable applications of synthetic division is its role in solving polynomial equations. By utilizing the remainder theorem, one can quickly determine whether a particular value is a root of the polynomial you seek to evaluate. If the remainder is 0 upon applying synthetic division, it confirms that the termed value is indeed another root of the function, thereby extending our root-finding efforts.
Using Synthetic Division for Evaluating Polynomials
Synthetic division is also instrumental in the evaluation of polynomials without extensive calculation. Instead of substituting the variable in the polynomial formula each time, applying the syntactical method allows for seamless evaluation of polynomial values across specified points. This adds to the flexibility and efficiency of working with complex polynomials.
Factoring Polynomials Using Synthetic Division
Additionally, synthetic division can assist in the factoring polynomials. By employing a known zero, creating synthetic division will enable you to break down higher-degree polynomials systematically. This method also complements other factoring strategies, enhancing overall polynomial identities and roots complexity for students and mathematics buffs alike.
Examples and Practice of Synthetic Division
Understanding synthetic division is straightforward with practice. Repeated exercises help grasp inadequate methodologies and uncover common pitfalls you may encounter.
Synthetic Division Examples
Let’s consider a polynomial: P(x) = 2x³ – 6x² + 4x – 12. If we are looking to divide this by (x – 3), our synthetic division setup would begin with:
1. Write 2, -6, 4, and -12 as coefficients.
2. Since we are using x – 3, we take r=3.
3. Follow the previous outlined steps yields: … (insert further calculations). Your final quotient and remainder will illustrate how effectively this method evaluates polynomial complexities.
Synthetic Division Worksheet and Resource Tools
You can find a plethora of synthetic division worksheets and interactive synthetic division calculator options online. They’ll serve as a great resource for practicing synthetic division with confirmation on the pathways you take in calculation.
Moreover, platforms dedicated to providing adjusted algebraic resources often foster understanding of synthetic division concepts by providing templates and guides for quick reference. Trying out various synthetic division examples can significantly solidify your confidence in applying this method in diverse algebraic settings.
Key Points to Remember
Synthetic division may appear daunting, but by overlaying the precise steps, it becomes less formidable. Here are key points to retain moving forward:
- Synthetic division is primarily used when dividing by linear factors.
- The remainder theorem aids in determining polynomial roots quickly.
- Regular practice through worksheets enhances proficiency and understanding of polynomial relations.
- Utilize resources and calculators available to ease the learning curve.
FAQ
1. What is synthetic division?
Synthetic division is a simplified method for dividing polynomials, particularly useful when dealing with linear divisors. It avoids the long steps of polynomial long division, allowing for faster calculations and easier management of coefficients.
2. When should I use synthetic division instead of long division?
Use synthetic division when you are dividing a polynomial by a linear divisor of the form (x – r). It’s particularly beneficial when you need to quickly determine roots or simplify calculations.
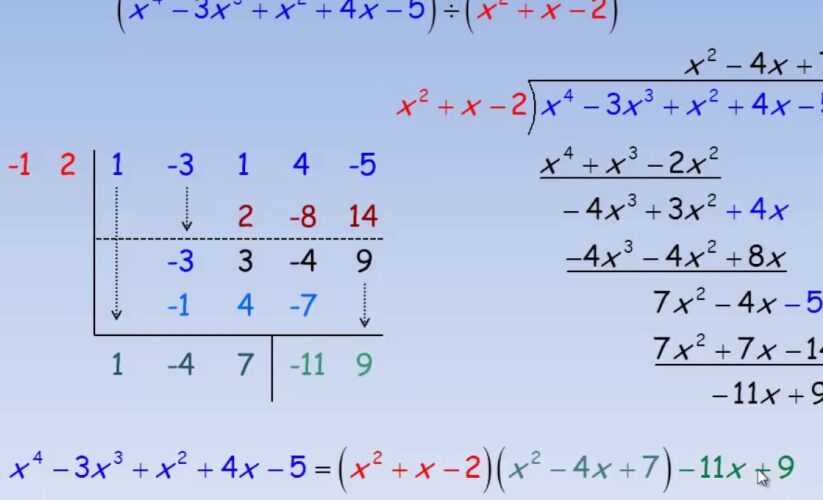
3. Can synthetic division be used for higher degree polynomials?
Yes, synthetic division is applicable to any polynomial as long as the divisor is linear. The method allows breaking down polynomials efficiently, regardless of their degree.
4. What is the role of the remainder in synthetic division?
The remainder in synthetic division represents what is left over after dividing one polynomial by another. If the remainder is zero, that means the divisor is a factor of the dividend polynomial.
5. How can I practice synthetic division more effectively?
To practice synthetic division effectively, use a combination of worksheets, online calculators, and tutorial videos. Regularly engage in real polynomial problems, and check your work to understand errors.
With this guide in hand, you are well on your path to mastering synthetic division and its applications in polynomial algebra. Start practicing today to enhance your skills by following the methods outlined above!