How to Properly Find Retained Earnings: A Complete Guide for 2025
How to Properly Find Retained Earnings: A Complete Guide for 2025
Understanding retained earnings is crucial for both business owners and financial professionals. Retained earnings represent the cumulative amount of net income that a company has kept, rather than distributed as dividends to shareholders. This guide will outline the various components of retained earnings, including its calculation, importance, and reporting methods, enabling you to effectively analyze this vital financial metric.
What Are Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings have significant implications for a company’s fiscal health. Defined as the portion of net income not paid out as dividends, retained earnings contribute to the equity section of a company’s balance sheet. They are used to fuel growth through reinvestment, pay down debt, or endure financial challenges. The understanding of retained earnings is enriched when examining their calculations, accounting practices, and strategies used for maximizing their benefits.
Retained Earnings Meaning in Finance
The meaning of retained earnings in finance involves understanding their role as a fundamental indicator of a company’s ongoing profitability. They highlight a business’s capacity to reinvest profit back into operations, which is often vital for long-term growth. Retained earnings can also reflect how management chooses to exercise fiscal prudence, maintaining financial stability instead of distributing earnings as dividends. Examples abound across various sectors, illustrating the strategic deployment of retained earnings toward new projects or enhancements in operational efficiency.
The Retained Earnings Formula
The retained earnings formula is straightforward and can be expressed as:
- Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends = Ending Retained Earnings
For instance, suppose a company starts the year with $100,000 in retained earnings, generates a net income of $50,000, and declares dividends of $20,000. Applying the formula yields:
- $100,000 + $50,000 – $20,000 = $130,000
This demonstrates how retained earnings effectively encompass the company’s financial performance across accounting periods, providing insight into growth potential.
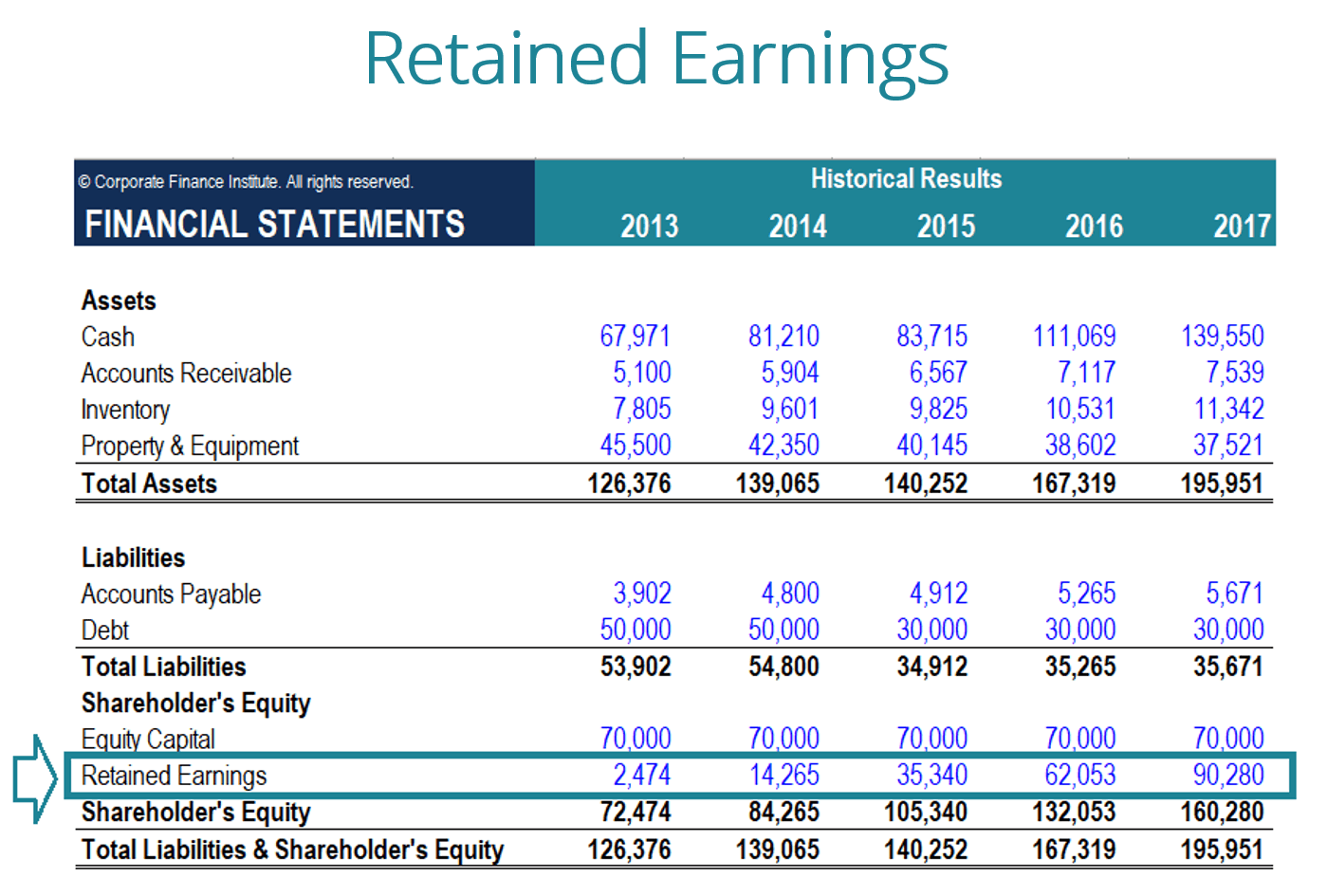
Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet
On the balance sheet, retained earnings are listed under the equity section, highlighting how much profit has been reinvested into the company. Monitoring the retained earnings over various periods can offer an investor insights into the company’s tactics for driving growth. It also enables stakeholders to assess the sustainability of management’s strategies. For instance, fluctuations in retained earnings might correlate with intensified operational strategies, altered dividend policies, or adjustments in financial performance.
How to Calculate Retained Earnings
Understanding how to calculate retained earnings is essential for accurate financial analysis. The calculation directly impacts various analytical techniques, including financial ratio analysis and forecasts. Businesses should regularly perform retained earnings calculations to gauge financial health and operational efficacy, as part of their ongoing financial reporting.
Retained Earnings Calculation Steps
The steps for effective retained earnings calculation include determining the initial retained earnings balance, adding net income accrued during the accounting period, and subtracting any dividends paid to shareholders. This process can be summed up as follows:
- Identify the starting retained earnings balance from the previous financial statement.
- Add the company’s net income from the current period.
- Subtract dividends declared and paid during that period.
This method ensures transparency and accuracy, fostering a clearer viewpoint of the company’s retained earnings dynamics. Utilizing consistency in these calculations dramatically enhances a business’s financial planning initiatives.
Practical Example of Retained Earnings Calculation
To better illustrate the retained earnings calculation example, let’s consider a company that begins the year with $200,000 in retained earnings. During the year, they generate $80,000 in net income and declare $30,000 in dividends. The calculation would be:
- $200,000 (beginning) + $80,000 (net income) – $30,000 (dividends) = $250,000 (ending retained earnings)
This demonstrates that through effective management of their profits and dividends, the company can substantially contribute to its retained earnings, laying a strong foundation for future investments and growth.
Understanding Retained Earnings Fluctuations
Fluctuations in retained earnings can result from several factors including changes in net income, alterations in dividend policies, and external financial challenges. These shifts can emerge from shifts in revenue streams, operational inefficiencies, or strategic pivots within the organization. Executing regular analysis can help stakeholders understand these changes and prepare for potential market uncertainties, informing future business decisions.
Importance of Retained Earnings in Business Strategy
The importance of retained earnings extends beyond simple calculations; they reflect strategic financial management decisions that can profoundly impact a company’s growth trajectory. Making informed choices leveraging retained earnings can lead to greater overall financial stability for organizations, assisting in investment opportunities and facilitating operational improvements.
Implementing Retained Earnings Policies
Establishing effective retained earnings policies is key to optimizing their management—balancing reinvestments against dividend distributions. An effective policy will consider the company’s priorities, including growth targets, shareholder expectations, and the current economic landscape. This can also include strategies to increase retained earnings, such as reinvesting profits into high-return projects or research and development.
Retained Earnings and Investment Opportunities
Characterized as a vital source of funds for many companies, retained earnings’s role in investment cannot be overlooked. By avoiding additional debt and using retained earnings, companies can finance operations, decrease liabilities, and enhance shareholder value. For instance, utilizing retained earnings to invest in new technology can improve efficiency or open newer markets.
Growth Analysis through Retained Earnings
Through examining trends in retained earnings growth, analysts and investors can deduce patterns that suggest business trajectory. Sustainable retained earnings growth typically indicates sound financial health and informed reinvestment strategies. Organizations often forecast their retained earnings based on projected net income and dividends, allowing them to assess funding abilities for upcoming initiatives.
Retained Earnings Reporting and Management
Managing retained earnings reporting is fundamental for transparent financial communications. Companies should aim to provide clarity and consistency in how they report retained earnings in financial statements.
Retained Earnings Audit Practices
Regular reviews and audits of retained earnings contribute to securing integrity and accuracy in financial reporting. Establishing robust retained earnings audit practices help ensure compliance and bolster stakeholder trust—creating a framework through which all financial reports can accurately reflect a company’s performance. A structured audit approach not only enhances credibility but also captures any discrepancies swiftly.
Retained Earnings Reporting Guidelines
Adhering to stringent retained earnings reporting guidelines is crucial for organizations. Investors rely heavily on these reports to gauge potential opportunities or risks associated with a company’s operations. Clear demarcation in net income, dividends, and retained earnings transitions should align with accepted accounting practices and standards to maintain transparency and promote investor confidence.
Adjustments in Retained Earnings Reporting
In cases where errors are uncovered, retained earnings adjustments may be required. These adjustments typically occur as the result of accounting errors or policy shifts within the company. Recording these adjustments accurately in financial statements is fundamental for compliance and maintaining accurate relationship between the company’s operational performance and reported financial position.
Key Takeaways
- Retained earnings are crucial for assessing financial health and future growth potential.
- Calculating retained earnings involves understanding the formula and related financial metrics.
- Effective retained earnings management strategies are essential to leverage growth opportunities.
- Regular audits and informed reporting practices promote accuracy and transparency.
- Monitoring trends can aid investors in spotting strategic shifts and operational efficiencies.
FAQ
1. What is the purpose of retained earnings?
The purpose of retained earnings is to serve as a source of internal funding for ongoing projects, debt management, and emerging opportunities. They indicate how a company reinvests profits instead of distributing them as dividends, demonstrating a commitment to growth and long-term sustainability.
2. How can I increase my company’s retained earnings?
To increase retained earnings, minimize dividend payouts, focus on boosting net profit through operational efficiency, and strategically reinvest profits into the business. This approach demonstrates a dedication to sustained growth, enabling improved financial health and stability.
3. Are retained earnings the same as retained profits?
Yes, retained earnings and retained profits refer to the same financial metric, highlighting accumulated net income that has not been distributed to shareholders. Both terms can be used interchangeably in accounting practices.
4. What are the characteristics of retained earnings?
Key characteristics of retained earnings include their reflection of past fiscal performance, the potential to influence future growth, variations in response to operational decisions, and their cumulative nature over time.
5. How do retained earnings impact a company’s valuation?
Retained earnings can significantly impact a company’s valuation. The accumulation of retained earnings indicates retained capital, which can signal strength in a business’s ability to sustain itself and invest in future initiatives. A business with strong retained earnings is often perceived as being less risky by investors.
6. What are some common adjustments made to retained earnings?
Common adjustments to retained earnings include correcting errors from previous financial statements, accounting for changes in accounting policies, and adjusting for stock buybacks. These practices ensure that retained earnings accurately reflect the company’s financial performance over time.
7. What is the relationship between retained earnings and dividends?
The relationship between retained earnings and dividends lies in the fact that dividends reduce retained earnings. Companies must consider their distributions carefully, as high dividends can limit sufficient growth capital. A balance must exist to foster shareholder satisfaction while ensuring strategic reinvestment.